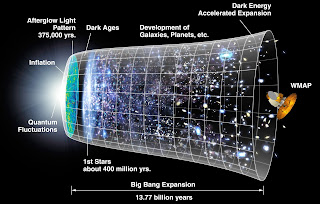
Soon after the big bang, followed by inflationary epoch, the universe was in a hot plasmonic state containing a mixture of radiation and baryons. The universe being in this fluid state made it possible for the pressure waves to travel. So, the universe had baryons and environment to support acoustic oscillations.